With imminent release of Windows 8, the buzzword has been Metro UI and Metro based applications. With Windows 8, Microsoft is introducing a new development platform called WinRT or Windows Runtime, that has developer community scratching its head.
Over 10 years ago Microsoft introduced the .NET framework which revolutionized Web Development at least for Microsoft developers. Those of us that were developing web based applications in classic ASP exhaled a sigh of relief. As framework matured, Visual Basic and C# matured as well.
Now with WinRT looming, most developers are wondering whether .NET framework is a thing of the past.
Similar to .NET Framework, WinRT is an intermediary and is built on top of COM. It allows you to develop applications using C#, VB.NET, XAML, but also in C++, HTML 5 and Javascript.
Admittedly there are some nice features, such as automatically deciding when to execute code in asynchronous mode rather than relying on developers, there are also some serious constraints - for example applications developed in WinRT will not run on previous versions of windows.
If you are wondering why another framework, why not just enhance .NET Framework to work with Metro apps? I am sure you are not alone.
Thank you.
Sunday, June 3, 2012
Saturday, May 19, 2012
Linq to Objects
In previous couple of posts we looked at the Linq to SQL i.e. using data context to get data from the database into an object collection. Today, we will look into using this object collection to filter data based on a certain criteria using Linq. If you haven't already figured it out, Linq is very similar to SQL except that the condition statements such as SELECT, WHERE etc. are reversed. Another requirement is that you must use aliases when writing Linq queries.
Let's look at an example. In this example, I am creating a customer class and creating a collection object (I have hard-coded values here, but in reality you will populate it from the database or other sources).
Once I have created an object collection, I can write Linq queries to filter the data. In this example, we are selecting all customers, filtering customers whose last name ends with a specific character and also ordering all customers by their last name. If you have more than one collection, you can create joins. In essence, you can write queries that are similar to T-SQL but they work on objects.
Main()
Customer Class
You should try out some other examples using joins etc.
Thank you.
Let's look at an example. In this example, I am creating a customer class and creating a collection object (I have hard-coded values here, but in reality you will populate it from the database or other sources).
Once I have created an object collection, I can write Linq queries to filter the data. In this example, we are selecting all customers, filtering customers whose last name ends with a specific character and also ordering all customers by their last name. If you have more than one collection, you can create joins. In essence, you can write queries that are similar to T-SQL but they work on objects.
Main()
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace LinqToObject
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//create a collection and call a method to populate this collection
List<Customer> customerList = new List<Customer>();
Customer cust = new Customer();
customerList = cust.createCollection();
//Now I have a collection called customerList of type Customer.
// Let's use Linq to get results from this collection
// Select all customers
SelectAllCustomers(customerList);
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
//Select all customers Ordered by LastName Desc.
SelectAllCustomersOrdered(customerList);
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
//Select a specific customer
SelectOneCustomer(customerList);
Console.Read();
}
static void SelectAllCustomers(List<Customer> customerList)
{
var customers = from d in customerList
select d;
foreach (var cust in customers)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}, {2}",
cust.FirstName + " " + cust.LastName,cust.Email,
cust.StreetAddress + ", " + cust.City + ", " +
cust.State + ", " + cust.ZipCode);
}
}
static void SelectAllCustomersOrdered(List<Customer> customerList)
{
var customers = from d in customerList
orderby d.LastName descending
select d;
foreach (var cust in customers)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}, {2}",
cust.FirstName + " " + cust.LastName, cust.Email,
cust.StreetAddress + ", " + cust.City + ", " +
cust.State + ", " + cust.ZipCode);
}
}
static void SelectOneCustomer(List<Customer> customerList)
{
var customers = from d in customerList
where d.FirstName.EndsWith("0")
select d;
foreach (var cust in customers)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}, {2}",
cust.FirstName + " " + cust.LastName, cust.Email,
cust.StreetAddress + ", " + cust.City + ", " +
cust.State + ", " + cust.ZipCode);
}
}
}
}
Customer Class
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace LinqToObject
{
class Customer
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string StreetAddress { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public string ZipCode { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Generate a Collection
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public List<Customer> createCollection()
{
List<Customer> custList = new List<Customer>();
for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++)
{
Customer cust = new Customer();
cust.FirstName="FN" + i.ToString();
cust.LastName="LN" + i.ToString();
cust.Email=cust.FirstName + "." + cust.LastName + "@mail.com";
cust.StreetAddress = "123" + i.ToString() + " Ross Rd";
cust.City = "Marietta";
cust.State = "GA";
cust.ZipCode = "12345";
custList.Add(cust);
}
return custList;
}
}
}
You should try out some other examples using joins etc.
Thank you.
Wednesday, May 16, 2012
Linq to SQL - Part II
In previous post we discussed how you can create DBML file and then use Linq to create SQL like queries to select the data from the database. In this post we will use the same project but see how you can use Linq to update, add and delete a record.
I have created a console app have methods for Select, Update, Add and Delete. Each method uses Linq queries to perform select, update, add and delete functions.
Finally, in Delete method, because my Customers table has a foreign key relationship with Customers_Audit table, I must first delete the record from the Customers_Audit table before deleting from the Customers table.
Let's review an example.
As you can see, it is fairly straightforward and works great for simple applications. It does get rather cumbersome in some cases and doesn't work in others as Linq to SQL only supports 1 to 1 mapping of tables, views etc. Entity framework is more suited for larger, complex applications. To create a DBML file to make your application aware of the underlying database schema, check out my previous post.
Thank you
I have created a console app have methods for Select, Update, Add and Delete. Each method uses Linq queries to perform select, update, add and delete functions.
Finally, in Delete method, because my Customers table has a foreign key relationship with Customers_Audit table, I must first delete the record from the Customers_Audit table before deleting from the Customers table.
Let's review an example.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
namespace LinqToSQL
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// DataContext takes a connection string
linqToSQLDataContext db = new linqToSQLDataContext();
//Select all customers and print them out
SelectCustomers(db);
//Update a customer's last name
UpdateCustomers(db);
//Add a new customer.
//I have a trigger on Customers table which also inserts the new record into
//Customers_Audit table
AddCustomers(db);
//Delete a Customer
//Since this table has a foreign key relationship with another table,
//I must delete record form both tables
DeleteCustomer(db);
Console.Read();
}
static void SelectCustomers(linqToSQLDataContext db)
{
var customerQuery = from d in db.Customers
orderby d.LastName
select d;
foreach (var cust in customerQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine("id = {0}, FirstName = {1},LastName = {2}",
cust.CustomerID, cust.FirstName, cust.LastName);
}
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
//getting data from multiple tables
var CustomersAndAddresses = from c in db.Customers
from o in db.CustomerAddresses
where c.CustomerID == o.CustomerID
where c.CustomerID == 1
select new { c.FirstName, c.LastName, o.Address1,
o.Address2, o.City, o.State };
foreach (var cust in CustomersAndAddresses)
{
Console.WriteLine("Name={0}, Address = {1},City = {2}",
cust.FirstName + ' ' + cust.LastName, cust.Address1 + ' ' +
cust.Address2, cust.City);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Update existing Customers
/// </summary>
static void UpdateCustomers(linqToSQLDataContext db)
{
var customerQuery = from d in db.Customers
orderby d.LastName where d.LastName == "Smith"
select d;
foreach (var cust in customerQuery)
{
cust.LastName = "Smithsonian";
}
db.SubmitChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Last Name Updated");
}
/// <summary>
/// Insert new Customers
/// </summary>
static void AddCustomers(linqToSQLDataContext db)
{
Customer newCustomer = new Customer();
newCustomer.FirstName="Sonny";
newCustomer.LastName="Hendrix";
newCustomer.EmailAddress = "sHendrix@mail.com";
db.Customers.InsertOnSubmit(newCustomer);
db.SubmitChanges();
db.SubmitChanges();
Console.WriteLine("New Customer Inserted");
}
/// <summary>
/// Delete existing Customer
/// </summary>
static void DeleteCustomer(linqToSQLDataContext db)
{
var customerAuditQuery = from a in db.Customers_Audits
orderby a.LastName
where a.LastName == "Hendrix"
select a;
var customerQuery = from d in db.Customers
orderby d.LastName
where d.LastName == "Hendrix"
select d;
db.Customers_Audits.DeleteAllOnSubmit(customerAuditQuery);
db.Customers.DeleteAllOnSubmit(customerQuery);
db.SubmitChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Hendrix Deleted");
}
}
}
As you can see, it is fairly straightforward and works great for simple applications. It does get rather cumbersome in some cases and doesn't work in others as Linq to SQL only supports 1 to 1 mapping of tables, views etc. Entity framework is more suited for larger, complex applications. To create a DBML file to make your application aware of the underlying database schema, check out my previous post.
Thank you
Thursday, May 10, 2012
Linq To SQL - Part I
In previous few posts we discussed entity framework and how you can use it to model your database tables/views/stored procedures and use them in your application. We also touched on Linq to Entities (more on this later).
Today we will review Linq to SQL. Linq to SQL is another way to work with your database instead of using entity framework. Linq to SQL is good for simple applications as it only supports 1 to 1 mapping of tables, views, procedures or UDFs.
Let's look at an example.
1. I created a console app and added Linq to SQL Classes dbml object.
2. Add the tables / views you want to generate classes for.
3. Now we will select the data from these tables using Linq to SQL.
As you can see in code above, we created two Linq to SQL queries - 1st one is getting data with just one table, the other one with both tables.
You can also add a WHERE clause similar to T-SQL. For example, I can modify above query
var CustomersAndAddresses = from c in db.Customers
from o in db.CustomerAddresses
WHERE c.CustomerID == o.CustomerID
WHERE c.CustomerID == 1
select new { c.FirstName,c.LastName, o.Address1,o.Address2,o.City,o.State };
In next post we will review how you can insert, update or delete a record using Linq to SQL.
Thank you.
Today we will review Linq to SQL. Linq to SQL is another way to work with your database instead of using entity framework. Linq to SQL is good for simple applications as it only supports 1 to 1 mapping of tables, views, procedures or UDFs.
Let's look at an example.
1. I created a console app and added Linq to SQL Classes dbml object.
3. Now we will select the data from these tables using Linq to SQL.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
namespace LinqToSQL
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// DataContext takes a connection string
linqToSQLDataContext db = new linqToSQLDataContext();
var customerQuery = from d in db.Customers
orderby d.LastName
select d;
foreach (var cust in customerQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine("id = {0}, FirstName = {1},LastName = {2}",
cust.CustomerID, cust.FirstName, cust.LastName);
}
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
//getting data from multiple tables
var CustomersAndAddresses = from c in db.Customers
from o in db.CustomerAddresses
select new { c.FirstName,c.LastName,
o.Address1,o.Address2,o.City,o.State };
foreach (var cust in CustomersAndAddresses)
{
Console.WriteLine("Name={0}, Address = {1},City = {2}",
cust.FirstName + ' ' + cust.LastName, cust.Address1 + ' ' +
cust.Address2, cust.City);
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}
As you can see in code above, we created two Linq to SQL queries - 1st one is getting data with just one table, the other one with both tables.
You can also add a WHERE clause similar to T-SQL. For example, I can modify above query
var CustomersAndAddresses = from c in db.Customers
from o in db.CustomerAddresses
WHERE c.CustomerID == o.CustomerID
WHERE c.CustomerID == 1
select new { c.FirstName,c.LastName, o.Address1,o.Address2,o.City,o.State };
In next post we will review how you can insert, update or delete a record using Linq to SQL.
Thank you.
Saturday, May 5, 2012
Entity Framework - Using Stored Procedure to Insert/Update/Delete
In previous post, we talked about using SELECT stored procedure with entity framework to get the results. In this post we will discuss how you can use Insert / Update / Delete stored procedures with entity framework. There are two ways to use stored procedures - one with using the object context and calling the stored procedure, passing parameters. Second method is by associating your stored procedures with the entity, which will result in the entity data model automatically calling the stored procedures when you call "SaveChanges" method.
We will look at the same example as before.
1. Open the EDMX file and select the table you want to associate your stored procedures with, right click and select "Stored Procedure Mapping"
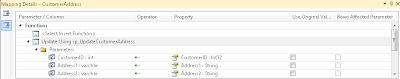
2. In the Mapping Details Pane, select the stored procedures for Insert, Update and Delete. Map any columns as necessary, although in most cases your columns should already be mapped appropriately. For Insert, if you are going to return the ID value back, map it to new field.
Note: For the model to work, you must associate all three functions i.e. Insert, Update and Delete.
Now, when you call .SaveChanges() method, any changes made to this table will automatically execute these stored procedures.
Here is the code.
Thank you.
We will look at the same example as before.
1. Open the EDMX file and select the table you want to associate your stored procedures with, right click and select "Stored Procedure Mapping"
2. In the Mapping Details Pane, select the stored procedures for Insert, Update and Delete. Map any columns as necessary, although in most cases your columns should already be mapped appropriately. For Insert, if you are going to return the ID value back, map it to new field.
Note: For the model to work, you must associate all three functions i.e. Insert, Update and Delete.
Now, when you call .SaveChanges() method, any changes made to this table will automatically execute these stored procedures.
Here is the code.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.Objects;
using System.Data.Objects.DataClasses;
namespace EntiryFramework
{
public partial class Main2 : Form
{
private OrdersEntities orders;
public Main2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Main2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
orders = new OrdersEntities();
var customerQuery = from d in orders.Customers.Include("CustomerAddresses")
orderby d.LastName
select d;
try
{
// Bind the ComboBox control to the query,
// which is executed during data binding.
// To prevent the query from being executed multiple times during binding,
// it is recommended to bind controls to the result of the Execute method.
this.customerList.DisplayMember = "LastName";
this.customerList.ValueMember = "CustomerID";
this.customerList.DataSource =
((ObjectQuery)customerQuery).Execute(MergeOption.AppendOnly);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private void customerList_SelectedIndexChanged_1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{ //lets get the addresses that are associated with the selected customer
Customer customer = (Customer)this.customerList.SelectedItem;
Addresses.DataSource = customer.CustomerAddresses;
Addresses.Columns["CustomerID"].Visible = false;
Addresses.Columns["AddressID"].Visible = false;
Addresses.Columns["Customer"].Visible = false;
Addresses.AllowUserToDeleteRows = false;
Addresses.AutoResizeColumns(DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.AllCells);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private void Close_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void saveChanges_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
// Save changes to the database,
// display a message, and refresh the form.
orders.SaveChanges();
MessageBox.Show("Changes saved to the database.");
this.Refresh();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
Thank you.
Thursday, May 3, 2012
Entity Framework - Using Stored Procedures
In previous post we discussed how you can use Entity Framework and use auto generated methods to perform CRUD operations. Although this may work for most simple applications, sometimes you have to have stored procedures either because database doesn't have well defined relationships and constraints or you need data dispersed in multiple tables. Similarly, you may want to use a stored procedure to insert/update multiple tables etc.
While not as straightforward as using EDM provided methods, you can still use stored procedures with entity framework. Today, we will use a SELECT stored procedure to get the results and bind it to our dropdown list just as we did in previous post.
In order to use stored procedures, first you will have to generate functions. As we reviewed in earlier post, when you generate EDM class, wizard gives you an option to select tables / views / stored procedures. Assuming you did, stored procedures are now part of the EDM class.
1. Double click on .edmx file to open it in design surface.
2. Right click anywhere on the surface then Add > Function Import
3. Name your function and select your stored procedure from the drop down.
4. If your stored procedure is not going to return anything (for example, inserting or updating a record) you can select None from Returns a Collection Of (None will return an integer value indicating whether script executed successfully or not). If your stored procedure is going to return a single value, you can select Scalar. But in most cases you will select Complex. If you select Complex you need to click on Get Column Information which will load all the columns returned by the stored procedure. Clicking on Create New Complex Type will create a new object where your stored proc. results will be loaded.
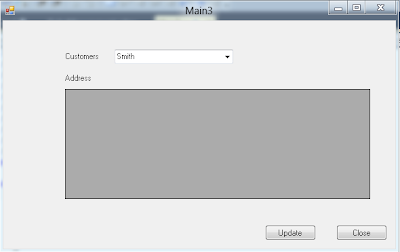
Now your stored procedure is wired up to be used in your code. The code below uses this stored procedure to return a collection and then we will bind this collection to drop down control.
When you run the project, you will see customers loaded in the drop down list
Don't worry about the grid view below. In next post we will use stored procedure to insert a new address and update an existing address.
Thank you.
While not as straightforward as using EDM provided methods, you can still use stored procedures with entity framework. Today, we will use a SELECT stored procedure to get the results and bind it to our dropdown list just as we did in previous post.
In order to use stored procedures, first you will have to generate functions. As we reviewed in earlier post, when you generate EDM class, wizard gives you an option to select tables / views / stored procedures. Assuming you did, stored procedures are now part of the EDM class.
1. Double click on .edmx file to open it in design surface.
2. Right click anywhere on the surface then Add > Function Import
4. If your stored procedure is not going to return anything (for example, inserting or updating a record) you can select None from Returns a Collection Of (None will return an integer value indicating whether script executed successfully or not). If your stored procedure is going to return a single value, you can select Scalar. But in most cases you will select Complex. If you select Complex you need to click on Get Column Information which will load all the columns returned by the stored procedure. Clicking on Create New Complex Type will create a new object where your stored proc. results will be loaded.
Now your stored procedure is wired up to be used in your code. The code below uses this stored procedure to return a collection and then we will bind this collection to drop down control.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.Objects;
using System.Data.Objects.DataClasses;
namespace EntiryFramework
{
public partial class Main3 : Form
{
private OrdersEntities orders;
public Main3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Main3_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
orders = new OrdersEntities();
List<SelectCustomers_Result> selectCustomers;
selectCustomers = orders.SelectCustomers().ToList();
try
{
// Bind the ComboBox control to the query,
// which is executed during data binding.
// To prevent the query from being executed multiple times during binding,
// it is recommended to bind controls to the result of the Execute method.
this.customerList.DisplayMember = "LastName";
this.customerList.ValueMember = "CustomerID";
this.customerList.DataSource = selectCustomers;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
When you run the project, you will see customers loaded in the drop down list
Don't worry about the grid view below. In next post we will use stored procedure to insert a new address and update an existing address.
Thank you.
Saturday, April 28, 2012
Entity Framework - Adding / Updating Records
In previous post we reviewed Entity Framework and how you can use Linq to entity to get the data from the database and bind it to a control.
In this post we will use the same project but go one step further - insert and update data using entity framework. Although this is rather simple example, you can still see the power of entity framework and how easy it is to perform database operations without writing much code.
In this example, instead of using read only text fields to load the address, we will load the addresses in a gridview which will allow us to add another address or edit an existing address.
I am using the same project from the previous post, so I already have entity framework objects configured. I created a new form with two controls - Combobox and a Gridview. When you run this project, combobox will load all the customers and selecting a name will load the selected customer's address(es) in the gridview
.
Running the Project
My grid is editable, so I can update an existing address or enter a new address. Once I modify an existing address or add a new address and click on Update, the code behind this button will save my changes and give me a confirmation message.
Let's review code.
Notice the code under "saveChanges_Click" method. orders.SaveChanges() is all it takes to save your changes - whether modifications to an existing address or adding new addresses.
For this to work, be sure your tables have a primary key. Without a primary key, this will not work. Also, you may get an error if your entity is mapped to a customized query or a view rather than a table.
Entity Framework allows you to map your database schema and have the framework generate the plumbing for you. But for this to truly work, you must have proper keys/referential integrity in your database tables and relationships between them.
Thank you.
In this post we will use the same project but go one step further - insert and update data using entity framework. Although this is rather simple example, you can still see the power of entity framework and how easy it is to perform database operations without writing much code.
In this example, instead of using read only text fields to load the address, we will load the addresses in a gridview which will allow us to add another address or edit an existing address.
I am using the same project from the previous post, so I already have entity framework objects configured. I created a new form with two controls - Combobox and a Gridview. When you run this project, combobox will load all the customers and selecting a name will load the selected customer's address(es) in the gridview
.
Running the Project
My grid is editable, so I can update an existing address or enter a new address. Once I modify an existing address or add a new address and click on Update, the code behind this button will save my changes and give me a confirmation message.
Let's review code.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.Objects;
using System.Data.Objects.DataClasses;
namespace EntiryFramework
{
public partial class Main2 : Form
{
private OrdersEntities orders;
public Main2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Main2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
orders = new OrdersEntities();
var customerQuery = from d in orders.Customers.Include("CustomerAddresses")
orderby d.LastName
select d;
try
{
// Bind the ComboBox control to the query,
// which is executed during data binding.
// To prevent the query from being executed multiple
//times during binding, it is recommended to bind
//controls to the result of the Execute method.
this.customerList.DisplayMember = "LastName";
this.customerList.ValueMember = "CustomerID";
this.customerList.DataSource =
((ObjectQuery)customerQuery).Execute(MergeOption.AppendOnly);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private void customerList_SelectedIndexChanged_1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
//lets get the addresses that are associated with the selected customer
Customer customer = (Customer)this.customerList.SelectedItem;
Addresses.DataSource = customer.CustomerAddresses;
Addresses.Columns["CustomerID"].Visible = false;
Addresses.Columns["AddressID"].Visible = false;
Addresses.Columns["Customer"].Visible = false;
Addresses.AllowUserToDeleteRows = false;
Addresses.AutoResizeColumns(DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.AllCells);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private void Close_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void saveChanges_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
// Save changes to the database,
// display a message, and refresh the form.
orders.SaveChanges();
MessageBox.Show("Changes saved to the database.");
this.Refresh();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
Notice the code under "saveChanges_Click" method. orders.SaveChanges() is all it takes to save your changes - whether modifications to an existing address or adding new addresses.
For this to work, be sure your tables have a primary key. Without a primary key, this will not work. Also, you may get an error if your entity is mapped to a customized query or a view rather than a table.
Entity Framework allows you to map your database schema and have the framework generate the plumbing for you. But for this to truly work, you must have proper keys/referential integrity in your database tables and relationships between them.
Thank you.
Wednesday, April 25, 2012
Entity Framework - Part II
In previous post we created a simple winform project and then generated an entity framework data model (EDM) using a small Orders database. Today, we will use the same project and query the data using entity framework from the underlying database and bind it to an element. If you haven't reviewed previous post, I strongly suggest you do so now.
In this example, we will use some of the built in methods such as List to get a list of customers and bind it to the dropdown list.
We will also use Linq to entities to get a list of addresses that are associated with the selected customer and load the address in read only text fields.
Example -
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.Objects;
using System.Data.Objects.DataClasses;
namespace EntiryFramework
{
public partial class Main : Form
{
private OrdersEntities orders;
public Main()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Close_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void Main_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Initialize the ObjectContext
orders = new OrdersEntities();
//Load all customers
List<Customer> customerList = orders.Customers.ToList();
try
{
//bind to the database
this.customerList.DisplayMember = "LastName";
this.customerList.ValueMember = "CustomerID";
this.customerList.DataSource = customerList;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private void customerList_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//lets get the addresses that are associated with the selected customer
int customerID = (int)this.customerList.SelectedValue;
IQueryable<CustomerAddress> customerAddress = orders.Customers
.Where(d => d.CustomerID == customerID)
.SelectMany(d => d.CustomerAddresses);
foreach (CustomerAddress address in customerAddress)
{
txtAddress1.Text = address.Address1;
txtAddress2.Text = address.Address2;
txtCity.Text = address.City;
txtState.Text = address.State;
txtZip.Text = address.ZipCode;
}
}
}
}
When you run this application, you will see something like this and as you change the customer name in the drop down list, the address will change.
var customerQuery = from d in orders.Customers
orderby d.LastName
select d;
try
{
// Bind the ComboBox control to the query,
// which is executed during data binding.
// To prevent the query from being executed multiple times during binding,
// it is recommended to bind controls to the result of the Execute method.
this.customerList.DisplayMember = "LastName";
this.customerList.ValueMember = "CustomerID";
this.customerList.DataSource = ((ObjectQuery)customerQuery)
.Execute(MergeOption.AppendOnly);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
In the next post we will update a customer using entity framework.
Thank you.
Saturday, April 21, 2012
Entity Framework - Part I
In previous post we touched briefly on entity framework and the benefits it provides. In this post we will walk through the process of creating an entity data model object in our project and then in future post use it to create a functional project. If you have worked with typed datasets, you will find the process very similar when it comes to generating the EDM files, but in my view, entity framework is much more powerful and simpler to use than typed datasets.
Lets create a test project and then create an entity data model file. We will use a sample database that I have created in my test environment.
We will create a simple Winform application and add a combobox to display all the customers in the database.
1. Add a Winform and a combo box to this form.
Add Entity Data Model
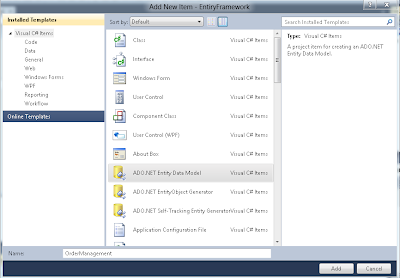
1. Right click on the Project and Add new Item. Select ADO.NET Entity Data Model
2. Select Generate from database and click on Next
3. Select the server and the database and click on OK
4.Make sure to check "Save Entity Connection Settings in App.Config" and pick a name
5. Click on Finish and a new EDM file is generated with extension edmx and a code behind file.
The edmx file looks like your database diagram (very similar to axd file)
6. If you open the code behind file, you will notice the framework has already abstracted your tables as classes and created a relationship between them.
This is lot of code, but the best thing is that you don't have to write any of it. Entity Framework automatically generates code, adding methods to add / update data in your database. Your business logic will work with this code rather than the database itself.
In the next post we will use this code to develop a functional project.
Thank you.
Lets create a test project and then create an entity data model file. We will use a sample database that I have created in my test environment.
We will create a simple Winform application and add a combobox to display all the customers in the database.
1. Add a Winform and a combo box to this form.
Add Entity Data Model
1. Right click on the Project and Add new Item. Select ADO.NET Entity Data Model
2. Select Generate from database and click on Next
3. Select the server and the database and click on OK
The edmx file looks like your database diagram (very similar to axd file)
6. If you open the code behind file, you will notice the framework has already abstracted your tables as classes and created a relationship between them.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// <auto-generated>
// This code was generated from a template.
//
// Manual changes to this file may cause unexpected behavior in your application.
// Manual changes to this file will be overwritten if the code is regenerated.
// </auto-generated>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data.EntityClient;
using System.Data.Objects;
using System.Data.Objects.DataClasses;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
[assembly: EdmSchemaAttribute()]
#region EDM Relationship Metadata
[assembly: EdmRelationshipAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "Customers", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.One, typeof(EntiryFramework.Customer), "CustomerAddress", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.Many, typeof(EntiryFramework.CustomerAddress), true)]
[assembly: EdmRelationshipAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_Orders_Customers", "Customers", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.One, typeof(EntiryFramework.Customer), "Orders", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.Many, typeof(EntiryFramework.Order), true)]
[assembly: EdmRelationshipAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_OrderDetails_Items", "Items", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.One, typeof(EntiryFramework.Item), "OrderDetails", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.Many, typeof(EntiryFramework.OrderDetail), true)]
[assembly: EdmRelationshipAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "Orders", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.One, typeof(EntiryFramework.Order), "OrderDetails", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.Many, typeof(EntiryFramework.OrderDetail), true)]
[assembly: EdmRelationshipAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "SalesPerson", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.ZeroOrOne, typeof(EntiryFramework.SalesPerson), "Orders", System.Data.Metadata.Edm.RelationshipMultiplicity.Many, typeof(EntiryFramework.Order), true)]
#endregion
namespace EntiryFramework
{
#region Contexts
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public partial class OrdersEntities : ObjectContext
{
#region Constructors
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new OrdersEntities object using the connection string found in the 'OrdersEntities' section of the application configuration file.
/// </summary>
public OrdersEntities() : base("name=OrdersEntities", "OrdersEntities")
{
this.ContextOptions.LazyLoadingEnabled = true;
OnContextCreated();
}
/// <summary>
/// Initialize a new OrdersEntities object.
/// </summary>
public OrdersEntities(string connectionString) : base(connectionString, "OrdersEntities")
{
this.ContextOptions.LazyLoadingEnabled = true;
OnContextCreated();
}
/// <summary>
/// Initialize a new OrdersEntities object.
/// </summary>
public OrdersEntities(EntityConnection connection) : base(connection, "OrdersEntities")
{
this.ContextOptions.LazyLoadingEnabled = true;
OnContextCreated();
}
#endregion
#region Partial Methods
partial void OnContextCreated();
#endregion
#region ObjectSet Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public ObjectSet<CustomerAddress> CustomerAddresses
{
get
{
if ((_CustomerAddresses == null))
{
_CustomerAddresses = base.CreateObjectSet<CustomerAddress>("CustomerAddresses");
}
return _CustomerAddresses;
}
}
private ObjectSet<CustomerAddress> _CustomerAddresses;
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public ObjectSet<Customer> Customers
{
get
{
if ((_Customers == null))
{
_Customers = base.CreateObjectSet<Customer>("Customers");
}
return _Customers;
}
}
private ObjectSet<Customer> _Customers;
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public ObjectSet<Item> Items
{
get
{
if ((_Items == null))
{
_Items = base.CreateObjectSet<Item>("Items");
}
return _Items;
}
}
private ObjectSet<Item> _Items;
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public ObjectSet<OrderDetail> OrderDetails
{
get
{
if ((_OrderDetails == null))
{
_OrderDetails = base.CreateObjectSet<OrderDetail>("OrderDetails");
}
return _OrderDetails;
}
}
private ObjectSet<OrderDetail> _OrderDetails;
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public ObjectSet<Order> Orders
{
get
{
if ((_Orders == null))
{
_Orders = base.CreateObjectSet<Order>("Orders");
}
return _Orders;
}
}
private ObjectSet<Order> _Orders;
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public ObjectSet<SalesPerson> SalesPersons
{
get
{
if ((_SalesPersons == null))
{
_SalesPersons = base.CreateObjectSet<SalesPerson>("SalesPersons");
}
return _SalesPersons;
}
}
private ObjectSet<SalesPerson> _SalesPersons;
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
public ObjectSet<sysdiagram> sysdiagrams
{
get
{
if ((_sysdiagrams == null))
{
_sysdiagrams = base.CreateObjectSet<sysdiagram>("sysdiagrams");
}
return _sysdiagrams;
}
}
private ObjectSet<sysdiagram> _sysdiagrams;
#endregion
#region AddTo Methods
/// <summary>
/// Deprecated Method for adding a new object to the CustomerAddresses EntitySet. Consider using the .Add method of the associated ObjectSet<T> property instead.
/// </summary>
public void AddToCustomerAddresses(CustomerAddress customerAddress)
{
base.AddObject("CustomerAddresses", customerAddress);
}
/// <summary>
/// Deprecated Method for adding a new object to the Customers EntitySet. Consider using the .Add method of the associated ObjectSet<T> property instead.
/// </summary>
public void AddToCustomers(Customer customer)
{
base.AddObject("Customers", customer);
}
/// <summary>
/// Deprecated Method for adding a new object to the Items EntitySet. Consider using the .Add method of the associated ObjectSet<T> property instead.
/// </summary>
public void AddToItems(Item item)
{
base.AddObject("Items", item);
}
/// <summary>
/// Deprecated Method for adding a new object to the OrderDetails EntitySet. Consider using the .Add method of the associated ObjectSet<T> property instead.
/// </summary>
public void AddToOrderDetails(OrderDetail orderDetail)
{
base.AddObject("OrderDetails", orderDetail);
}
/// <summary>
/// Deprecated Method for adding a new object to the Orders EntitySet. Consider using the .Add method of the associated ObjectSet<T> property instead.
/// </summary>
public void AddToOrders(Order order)
{
base.AddObject("Orders", order);
}
/// <summary>
/// Deprecated Method for adding a new object to the SalesPersons EntitySet. Consider using the .Add method of the associated ObjectSet<T> property instead.
/// </summary>
public void AddToSalesPersons(SalesPerson salesPerson)
{
base.AddObject("SalesPersons", salesPerson);
}
/// <summary>
/// Deprecated Method for adding a new object to the sysdiagrams EntitySet. Consider using the .Add method of the associated ObjectSet<T> property instead.
/// </summary>
public void AddTosysdiagrams(sysdiagram sysdiagram)
{
base.AddObject("sysdiagrams", sysdiagram);
}
#endregion
}
#endregion
#region Entities
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmEntityTypeAttribute(NamespaceName="OrdersModel", Name="Customer")]
[Serializable()]
[DataContractAttribute(IsReference=true)]
public partial class Customer : EntityObject
{
#region Factory Method
/// <summary>
/// Create a new Customer object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="customerID">Initial value of the CustomerID property.</param>
public static Customer CreateCustomer(global::System.Int32 customerID)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.CustomerID = customerID;
return customer;
}
#endregion
#region Primitive Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 CustomerID
{
get
{
return _CustomerID;
}
set
{
if (_CustomerID != value)
{
OnCustomerIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("CustomerID");
_CustomerID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("CustomerID");
OnCustomerIDChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _CustomerID;
partial void OnCustomerIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnCustomerIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String FirstName
{
get
{
return _FirstName;
}
set
{
OnFirstNameChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("FirstName");
_FirstName = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("FirstName");
OnFirstNameChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _FirstName;
partial void OnFirstNameChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnFirstNameChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String LastName
{
get
{
return _LastName;
}
set
{
OnLastNameChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("LastName");
_LastName = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("LastName");
OnLastNameChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _LastName;
partial void OnLastNameChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnLastNameChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String EmailAddress
{
get
{
return _EmailAddress;
}
set
{
OnEmailAddressChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("EmailAddress");
_EmailAddress = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("EmailAddress");
OnEmailAddressChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _EmailAddress;
partial void OnEmailAddressChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnEmailAddressChanged();
#endregion
#region Navigation Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "CustomerAddress")]
public EntityCollection<CustomerAddress> CustomerAddresses
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedCollection<CustomerAddress>("OrdersModel.FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "CustomerAddress");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedCollection<CustomerAddress>("OrdersModel.FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "CustomerAddress", value);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_Orders_Customers", "Orders")]
public EntityCollection<Order> Orders
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedCollection<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_Customers", "Orders");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedCollection<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_Customers", "Orders", value);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmEntityTypeAttribute(NamespaceName="OrdersModel", Name="CustomerAddress")]
[Serializable()]
[DataContractAttribute(IsReference=true)]
public partial class CustomerAddress : EntityObject
{
#region Factory Method
/// <summary>
/// Create a new CustomerAddress object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="addressID">Initial value of the AddressID property.</param>
/// <param name="customerID">Initial value of the CustomerID property.</param>
public static CustomerAddress CreateCustomerAddress(global::System.Int32 addressID, global::System.Int32 customerID)
{
CustomerAddress customerAddress = new CustomerAddress();
customerAddress.AddressID = addressID;
customerAddress.CustomerID = customerID;
return customerAddress;
}
#endregion
#region Primitive Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 AddressID
{
get
{
return _AddressID;
}
set
{
if (_AddressID != value)
{
OnAddressIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("AddressID");
_AddressID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("AddressID");
OnAddressIDChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _AddressID;
partial void OnAddressIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnAddressIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 CustomerID
{
get
{
return _CustomerID;
}
set
{
if (_CustomerID != value)
{
OnCustomerIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("CustomerID");
_CustomerID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("CustomerID");
OnCustomerIDChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _CustomerID;
partial void OnCustomerIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnCustomerIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String Address1
{
get
{
return _Address1;
}
set
{
OnAddress1Changing(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("Address1");
_Address1 = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("Address1");
OnAddress1Changed();
}
}
private global::System.String _Address1;
partial void OnAddress1Changing(global::System.String value);
partial void OnAddress1Changed();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String Address2
{
get
{
return _Address2;
}
set
{
OnAddress2Changing(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("Address2");
_Address2 = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("Address2");
OnAddress2Changed();
}
}
private global::System.String _Address2;
partial void OnAddress2Changing(global::System.String value);
partial void OnAddress2Changed();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String City
{
get
{
return _City;
}
set
{
OnCityChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("City");
_City = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("City");
OnCityChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _City;
partial void OnCityChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnCityChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String State
{
get
{
return _State;
}
set
{
OnStateChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("State");
_State = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("State");
OnStateChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _State;
partial void OnStateChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnStateChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String ZipCode
{
get
{
return _ZipCode;
}
set
{
OnZipCodeChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("ZipCode");
_ZipCode = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("ZipCode");
OnZipCodeChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _ZipCode;
partial void OnZipCodeChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnZipCodeChanged();
#endregion
#region Navigation Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "Customers")]
public Customer Customer
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "Customers").Value;
}
set
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "Customers").Value = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[BrowsableAttribute(false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public EntityReference<Customer> CustomerReference
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "Customers");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_CustomerAddress_Customers", "Customers", value);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmEntityTypeAttribute(NamespaceName="OrdersModel", Name="Item")]
[Serializable()]
[DataContractAttribute(IsReference=true)]
public partial class Item : EntityObject
{
#region Factory Method
/// <summary>
/// Create a new Item object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="itemID">Initial value of the ItemID property.</param>
public static Item CreateItem(global::System.Int32 itemID)
{
Item item = new Item();
item.ItemID = itemID;
return item;
}
#endregion
#region Primitive Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 ItemID
{
get
{
return _ItemID;
}
set
{
if (_ItemID != value)
{
OnItemIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("ItemID");
_ItemID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("ItemID");
OnItemIDChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _ItemID;
partial void OnItemIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnItemIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String Description
{
get
{
return _Description;
}
set
{
OnDescriptionChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("Description");
_Description = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("Description");
OnDescriptionChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _Description;
partial void OnDescriptionChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnDescriptionChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Int32> QuantityOnHand
{
get
{
return _QuantityOnHand;
}
set
{
OnQuantityOnHandChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("QuantityOnHand");
_QuantityOnHand = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("QuantityOnHand");
OnQuantityOnHandChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Int32> _QuantityOnHand;
partial void OnQuantityOnHandChanging(Nullable<global::System.Int32> value);
partial void OnQuantityOnHandChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Decimal> SalesPrice
{
get
{
return _SalesPrice;
}
set
{
OnSalesPriceChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("SalesPrice");
_SalesPrice = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("SalesPrice");
OnSalesPriceChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Decimal> _SalesPrice;
partial void OnSalesPriceChanging(Nullable<global::System.Decimal> value);
partial void OnSalesPriceChanged();
#endregion
#region Navigation Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_OrderDetails_Items", "OrderDetails")]
public EntityCollection<OrderDetail> OrderDetails
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedCollection<OrderDetail>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Items", "OrderDetails");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedCollection<OrderDetail>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Items", "OrderDetails", value);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmEntityTypeAttribute(NamespaceName="OrdersModel", Name="Order")]
[Serializable()]
[DataContractAttribute(IsReference=true)]
public partial class Order : EntityObject
{
#region Factory Method
/// <summary>
/// Create a new Order object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="orderID">Initial value of the OrderID property.</param>
/// <param name="customerID">Initial value of the CustomerID property.</param>
public static Order CreateOrder(global::System.Int32 orderID, global::System.Int32 customerID)
{
Order order = new Order();
order.OrderID = orderID;
order.CustomerID = customerID;
return order;
}
#endregion
#region Primitive Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 OrderID
{
get
{
return _OrderID;
}
set
{
if (_OrderID != value)
{
OnOrderIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("OrderID");
_OrderID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("OrderID");
OnOrderIDChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _OrderID;
partial void OnOrderIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnOrderIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 CustomerID
{
get
{
return _CustomerID;
}
set
{
OnCustomerIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("CustomerID");
_CustomerID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("CustomerID");
OnCustomerIDChanged();
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _CustomerID;
partial void OnCustomerIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnCustomerIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Int32> SalesPersonID
{
get
{
return _SalesPersonID;
}
set
{
OnSalesPersonIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("SalesPersonID");
_SalesPersonID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("SalesPersonID");
OnSalesPersonIDChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Int32> _SalesPersonID;
partial void OnSalesPersonIDChanging(Nullable<global::System.Int32> value);
partial void OnSalesPersonIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Decimal> OrderAmount
{
get
{
return _OrderAmount;
}
set
{
OnOrderAmountChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("OrderAmount");
_OrderAmount = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("OrderAmount");
OnOrderAmountChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Decimal> _OrderAmount;
partial void OnOrderAmountChanging(Nullable<global::System.Decimal> value);
partial void OnOrderAmountChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Decimal> SalesTax
{
get
{
return _SalesTax;
}
set
{
OnSalesTaxChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("SalesTax");
_SalesTax = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("SalesTax");
OnSalesTaxChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Decimal> _SalesTax;
partial void OnSalesTaxChanging(Nullable<global::System.Decimal> value);
partial void OnSalesTaxChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Int32> OrderStatusID
{
get
{
return _OrderStatusID;
}
set
{
OnOrderStatusIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("OrderStatusID");
_OrderStatusID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("OrderStatusID");
OnOrderStatusIDChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Int32> _OrderStatusID;
partial void OnOrderStatusIDChanging(Nullable<global::System.Int32> value);
partial void OnOrderStatusIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.DateTime> OrderDate
{
get
{
return _OrderDate;
}
set
{
OnOrderDateChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("OrderDate");
_OrderDate = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("OrderDate");
OnOrderDateChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.DateTime> _OrderDate;
partial void OnOrderDateChanging(Nullable<global::System.DateTime> value);
partial void OnOrderDateChanged();
#endregion
#region Navigation Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_Orders_Customers", "Customers")]
public Customer Customer
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_Customers", "Customers").Value;
}
set
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_Customers", "Customers").Value = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[BrowsableAttribute(false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public EntityReference<Customer> CustomerReference
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_Customers", "Customers");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedReference<Customer>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_Customers", "Customers", value);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "OrderDetails")]
public EntityCollection<OrderDetail> OrderDetails
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedCollection<OrderDetail>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "OrderDetails");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedCollection<OrderDetail>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "OrderDetails", value);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "SalesPerson")]
public SalesPerson SalesPerson
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<SalesPerson>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "SalesPerson").Value;
}
set
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<SalesPerson>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "SalesPerson").Value = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[BrowsableAttribute(false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public EntityReference<SalesPerson> SalesPersonReference
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<SalesPerson>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "SalesPerson");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedReference<SalesPerson>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "SalesPerson", value);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmEntityTypeAttribute(NamespaceName="OrdersModel", Name="OrderDetail")]
[Serializable()]
[DataContractAttribute(IsReference=true)]
public partial class OrderDetail : EntityObject
{
#region Factory Method
/// <summary>
/// Create a new OrderDetail object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="orderDetailID">Initial value of the OrderDetailID property.</param>
/// <param name="orderID">Initial value of the OrderID property.</param>
/// <param name="itemID">Initial value of the ItemID property.</param>
/// <param name="quantity">Initial value of the Quantity property.</param>
public static OrderDetail CreateOrderDetail(global::System.Int32 orderDetailID, global::System.Int32 orderID, global::System.Int32 itemID, global::System.Int32 quantity)
{
OrderDetail orderDetail = new OrderDetail();
orderDetail.OrderDetailID = orderDetailID;
orderDetail.OrderID = orderID;
orderDetail.ItemID = itemID;
orderDetail.Quantity = quantity;
return orderDetail;
}
#endregion
#region Primitive Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 OrderDetailID
{
get
{
return _OrderDetailID;
}
set
{
if (_OrderDetailID != value)
{
OnOrderDetailIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("OrderDetailID");
_OrderDetailID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("OrderDetailID");
OnOrderDetailIDChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _OrderDetailID;
partial void OnOrderDetailIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnOrderDetailIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 OrderID
{
get
{
return _OrderID;
}
set
{
OnOrderIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("OrderID");
_OrderID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("OrderID");
OnOrderIDChanged();
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _OrderID;
partial void OnOrderIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnOrderIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 ItemID
{
get
{
return _ItemID;
}
set
{
OnItemIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("ItemID");
_ItemID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("ItemID");
OnItemIDChanged();
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _ItemID;
partial void OnItemIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnItemIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 Quantity
{
get
{
return _Quantity;
}
set
{
OnQuantityChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("Quantity");
_Quantity = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("Quantity");
OnQuantityChanged();
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _Quantity;
partial void OnQuantityChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnQuantityChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Decimal> UnitPrice
{
get
{
return _UnitPrice;
}
set
{
OnUnitPriceChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("UnitPrice");
_UnitPrice = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("UnitPrice");
OnUnitPriceChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Decimal> _UnitPrice;
partial void OnUnitPriceChanging(Nullable<global::System.Decimal> value);
partial void OnUnitPriceChanged();
#endregion
#region Navigation Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_OrderDetails_Items", "Items")]
public Item Item
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Item>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Items", "Items").Value;
}
set
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Item>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Items", "Items").Value = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[BrowsableAttribute(false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public EntityReference<Item> ItemReference
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Item>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Items", "Items");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedReference<Item>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Items", "Items", value);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "Orders")]
public Order Order
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "Orders").Value;
}
set
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "Orders").Value = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[BrowsableAttribute(false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public EntityReference<Order> OrderReference
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedReference<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "Orders");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedReference<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_OrderDetails_Orders", "Orders", value);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmEntityTypeAttribute(NamespaceName="OrdersModel", Name="SalesPerson")]
[Serializable()]
[DataContractAttribute(IsReference=true)]
public partial class SalesPerson : EntityObject
{
#region Factory Method
/// <summary>
/// Create a new SalesPerson object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="salesPersonID">Initial value of the SalesPersonID property.</param>
public static SalesPerson CreateSalesPerson(global::System.Int32 salesPersonID)
{
SalesPerson salesPerson = new SalesPerson();
salesPerson.SalesPersonID = salesPersonID;
return salesPerson;
}
#endregion
#region Primitive Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 SalesPersonID
{
get
{
return _SalesPersonID;
}
set
{
if (_SalesPersonID != value)
{
OnSalesPersonIDChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("SalesPersonID");
_SalesPersonID = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("SalesPersonID");
OnSalesPersonIDChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _SalesPersonID;
partial void OnSalesPersonIDChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void OnSalesPersonIDChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String FirstName
{
get
{
return _FirstName;
}
set
{
OnFirstNameChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("FirstName");
_FirstName = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("FirstName");
OnFirstNameChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _FirstName;
partial void OnFirstNameChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnFirstNameChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String LastName
{
get
{
return _LastName;
}
set
{
OnLastNameChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("LastName");
_LastName = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("LastName");
OnLastNameChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _LastName;
partial void OnLastNameChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnLastNameChanged();
#endregion
#region Navigation Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[XmlIgnoreAttribute()]
[SoapIgnoreAttribute()]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
[EdmRelationshipNavigationPropertyAttribute("OrdersModel", "FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "Orders")]
public EntityCollection<Order> Orders
{
get
{
return ((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.GetRelatedCollection<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "Orders");
}
set
{
if ((value != null))
{
((IEntityWithRelationships)this).RelationshipManager.InitializeRelatedCollection<Order>("OrdersModel.FK_Orders_SalesPerson", "Orders", value);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmEntityTypeAttribute(NamespaceName="OrdersModel", Name="sysdiagram")]
[Serializable()]
[DataContractAttribute(IsReference=true)]
public partial class sysdiagram : EntityObject
{
#region Factory Method
/// <summary>
/// Create a new sysdiagram object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name">Initial value of the name property.</param>
/// <param name="principal_id">Initial value of the principal_id property.</param>
/// <param name="diagram_id">Initial value of the diagram_id property.</param>
public static sysdiagram Createsysdiagram(global::System.String name, global::System.Int32 principal_id, global::System.Int32 diagram_id)
{
sysdiagram sysdiagram = new sysdiagram();
sysdiagram.name = name;
sysdiagram.principal_id = principal_id;
sysdiagram.diagram_id = diagram_id;
return sysdiagram;
}
#endregion
#region Primitive Properties
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.String name
{
get
{
return _name;
}
set
{
OnnameChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("name");
_name = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, false);
ReportPropertyChanged("name");
OnnameChanged();
}
}
private global::System.String _name;
partial void OnnameChanging(global::System.String value);
partial void OnnameChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 principal_id
{
get
{
return _principal_id;
}
set
{
Onprincipal_idChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("principal_id");
_principal_id = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("principal_id");
Onprincipal_idChanged();
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _principal_id;
partial void Onprincipal_idChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void Onprincipal_idChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=true, IsNullable=false)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Int32 diagram_id
{
get
{
return _diagram_id;
}
set
{
if (_diagram_id != value)
{
Ondiagram_idChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("diagram_id");
_diagram_id = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("diagram_id");
Ondiagram_idChanged();
}
}
}
private global::System.Int32 _diagram_id;
partial void Ondiagram_idChanging(global::System.Int32 value);
partial void Ondiagram_idChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public Nullable<global::System.Int32> version
{
get
{
return _version;
}
set
{
OnversionChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("version");
_version = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value);
ReportPropertyChanged("version");
OnversionChanged();
}
}
private Nullable<global::System.Int32> _version;
partial void OnversionChanging(Nullable<global::System.Int32> value);
partial void OnversionChanged();
/// <summary>
/// No Metadata Documentation available.
/// </summary>
[EdmScalarPropertyAttribute(EntityKeyProperty=false, IsNullable=true)]
[DataMemberAttribute()]
public global::System.Byte[] definition
{
get
{
return StructuralObject.GetValidValue(_definition);
}
set
{
OndefinitionChanging(value);
ReportPropertyChanging("definition");
_definition = StructuralObject.SetValidValue(value, true);
ReportPropertyChanged("definition");
OndefinitionChanged();
}
}
private global::System.Byte[] _definition;
partial void OndefinitionChanging(global::System.Byte[] value);
partial void OndefinitionChanged();
#endregion
}
#endregion
}
This is lot of code, but the best thing is that you don't have to write any of it. Entity Framework automatically generates code, adding methods to add / update data in your database. Your business logic will work with this code rather than the database itself.
In the next post we will use this code to develop a functional project.
Thank you.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)